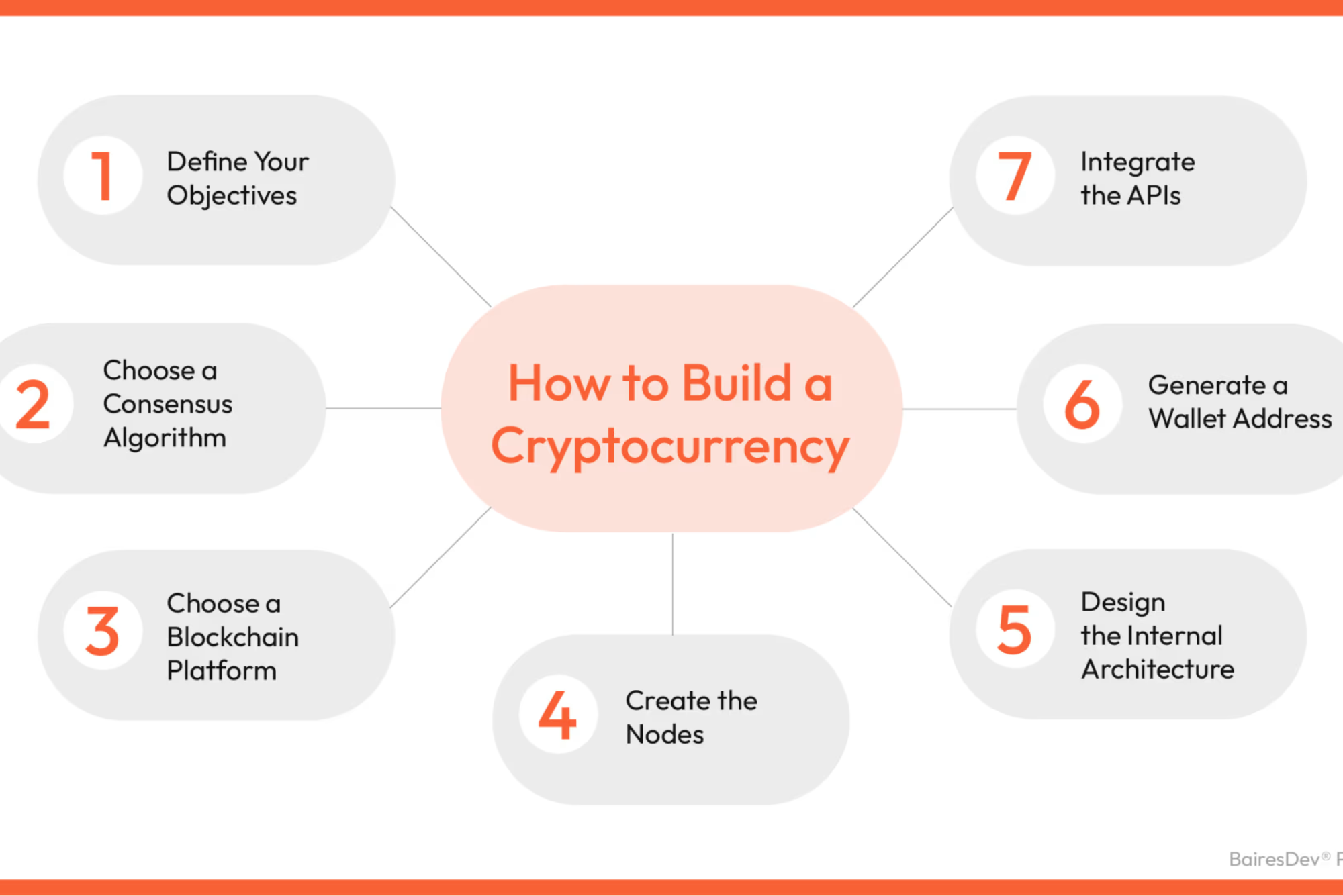
how to create your own cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the financial world, offering decentralized and secure transactions. If you’ve ever wondered how to create your own cryptocurrency, you’re in the right place. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process step-by-step.
Cryptocurrency
Before diving into creating your cryptocurrency, it’s crucial to understand the fundamentals. We’ll cover the basics of blockchain technology, consensus mechanisms, and the role of cryptocurrencies in the digital economy.
Planning Your Cryptocurrency
Creating a cryptocurrency requires create your own cryptocurrency meticulous planning. We’ll discuss defining your objectives, choosing the right blockchain platform, determining supply, and establishing governance models.
Development Process
The development phase involves coding your cryptocurrency’s protocol, creating the genesis block, and implementing necessary features like wallets and mining mechanisms. We’ll explore popular programming languages and development frameworks.
Security Measures
Security is paramount in the world of cryptocurrency. We’ll delve into best practices for securing your blockchain network, including encryption techniques, multi-signature wallets, and protection against common cyber threats.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid regulatory issues. We’ll outline the legal aspects of creating a cryptocurrency, including licensing requirements and regulatory frameworks.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Comprehensive Overview
Legal and regulatory compliance refers to the adherence of organizations, businesses, and individuals to the laws, rules, and regulations set forth by governmental bodies, industry standards, and other authoritative entities. It is a critical aspect of running any business or institution, ensuring that operations are conducted ethically, safely, and in accordance with the applicable laws. Failure to comply with these requirements can lead to legal consequences, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
1. What is Legal Compliance?
Legal compliance refers to the process of ensuring that a business or organization abides by the laws and regulations specific to its industry and location. These laws can be at the local, state, national, or even international levels, depending on where the business operates. For example, a company working in multiple countries may need to adhere to labor laws in each location, while also following international trade laws.
Legal compliance involves:
- Understanding the applicable laws: Different industries have different legal obligations, such as labor laws, safety standards, and environmental regulations. It’s crucial for businesses to be aware of these laws and incorporate them into their operational practices.
- Implementing necessary processes: Companies must develop policies, procedures, and training programs to ensure that their employees and management comply with the legal requirements.
- Monitoring and enforcement: Legal compliance is an ongoing process, requiring regular audits and monitoring to ensure continuous adherence to the law.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Industry-Specific Requirements
Regulatory compliance focuses on adhering to the rules and standards set by industry-specific regulatory bodies. These standards are often designed to protect public health, safety, and welfare. Regulatory compliance is essential for industries such as finance, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing, where strict guidelines are imposed by various authorities.
a. Financial Services
In the financial sector, regulatory compliance involves adhering to the regulations established by entities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), and other international financial authorities. Financial institutions must comply with anti-money laundering (AML) laws, data privacy regulations, and risk management requirements.
b. Healthcare
Healthcare compliance ensures that organizations in the medical field follow the rules set by governing bodies like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. Compliance in healthcare is critical for maintaining patient confidentiality, ensuring data security, and preventing healthcare fraud. Healthcare providers are also required to follow clinical guidelines, such as proper patient care protocols and medication administration.
c. Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical companies face a myriad of regulatory requirements from bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). These organizations enforce strict guidelines on drug development, testing, manufacturing, and distribution to ensure the safety and efficacy of medications.
3. Key Elements of Compliance Programs
For a business to ensure legal and regulatory compliance, they must have a well-defined compliance program in place. A strong compliance program typically includes the following elements:
a. Risk Assessment
Businesses must evaluate potential risks to their legal and regulatory obligations. This process involves identifying the most significant risks based on the organization’s industry, location, and business activities. By understanding their exposure to legal liabilities, businesses can focus on mitigating these risks through compliance measures.
b. Internal Policies and Procedures
A compliance program should establish clear internal policies that align with legal and regulatory requirements. These policies cover a wide range of areas such as employee behavior, financial reporting, health and safety practices, and data protection. Employees must be made aware of these policies through formal documentation and training programs.
c. Training and Awareness
Continuous employee training is essential to ensure that staff members understand their legal and regulatory obligations. Many organizations invest in annual training programs or compliance certifications for their employees. A culture of compliance must be fostered within the organization so that all employees understand the importance of adhering to the rules.
d. Monitoring and Auditing
A compliance program should include mechanisms for monitoring business activities and conducting regular audits. This helps identify any areas of non-compliance and allows organizations to take corrective actions before facing legal repercussions. Many companies have a dedicated compliance officer or team responsible for this function.
e. Enforcement and Accountability
Effective compliance programs ensure that violations are addressed and that the organization is held accountable for any breaches. This may involve disciplinary actions for employees who fail to comply with internal policies, or more formal consequences, such as fines and lawsuits, if the company fails to meet legal requirements.
4. The Role of Technology in Compliance
Technology plays an increasingly important role in legal and regulatory compliance, particularly in industries with complex requirements. Compliance management software allows organizations to automate many aspects of their compliance programs, from tracking employee certifications to managing legal documentation.
a. Data Privacy and Security
One of the major areas of regulatory concern is data privacy and security, especially with the rise of digital technologies and the internet. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. have set stringent rules for how companies must handle personal data.
b. Automated Monitoring
Automation tools can assist in real-time monitoring of compliance with legal requirements. For instance, financial institutions often use automated systems to track transactions for potential violations of anti-money laundering regulations.
5. Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with legal and regulatory requirements can have severe consequences for businesses and organizations. These include:
a. Fines and Penalties
Failure to comply with legal requirements can result in substantial fines and penalties from regulatory authorities. These financial penalties can be particularly damaging for smaller companies and may even lead to business closure.
b. Legal Action
Non-compliance can lead to lawsuits, both from governmental bodies and from private individuals or other companies. Legal battles are often costly and time-consuming, potentially damaging an organization’s reputation and financial standing.
c. Reputational Damage
In today’s world of social media and instant communication, reputational damage can spread quickly if a company is found in violation of legal or regulatory requirements. Negative publicity may result in a loss of consumer trust, decreased market share, and challenges in attracting new customers or business partners.
6. Global Compliance Challenges
Globalization presents unique challenges to legal and regulatory compliance. Businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions must navigate a complex web of laws and regulations, which may vary significantly from one country to another. Moreover, multinational companies must deal with varying enforcement practices and regulatory bodies across different regions.
For example, a company operating in both the U.S. and the European Union must comply with GDPR’s stringent data protection requirements while also adhering to the U.S. Federal Trade Commission’s consumer protection laws. Navigating these complexities requires a deep understanding of international law and a robust compliance framework.
7. The Future of Legal and Regulatory Compliance
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, businesses must stay ahead of new developments to ensure ongoing compliance. Trends like the increased focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards and the rise of artificial intelligence in compliance management are shaping the future of this critical business area.
In addition, governments worldwide are enhancing their enforcement mechanisms, meaning that companies will face greater scrutiny. Compliance will no longer be viewed as a box-ticking exercise but as a core element of responsible business practices.
Marketing and Launch Strategy
Launching your cryptocurrency successfully requires a solid marketing and launch strategy. We’ll discuss building a community, creating buzz through social media and PR, and executing a successful ICO or token sale.

Post-Launch Maintenance
After the launch, ongoing maintenance is essential to ensure the stability and success of your cryptocurrency. We’ll cover regular updates, bug fixes, community management, and scalability solutions.
Creating your cryptocurrency is a challenging yet rewarding endeavor. With the right knowledge and guidance, you can turn your vision into reality. Follow this comprehensive guide to embark on your journey into the world of digital currencies.
cryptocurrency news in hindi
Cryptocurrency news in India garners significant attention as regulations, market trends, and investor sentiments fluctuate. Updates on Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital assets are closely followed by a growing number of enthusiasts and investors. Discussions often revolve around regulatory developments, market analysis, and the impact of global events on the Indian crypto landscape.